What is a combinatorial (counting) argument for the identity [math]{2n \choose n} = \sum_{i=0}^{n} {n \choose i}^2[/math]? - Quora

ordinary differential equations - Formulas's deduction from the generating function of Hermite polynomials - Mathematics Stack Exchange

PDF) Generating functions involving binomial coefficients \({4n\choose 2n}\), it's squared, reciprocal and their closed forms for hypergeometric expressions.

combinatorics - Combinatorial proof of summation of $\sum\limits_{k = 0}^n { n \choose k}^2= {2n \choose n}$ - Mathematics Stack Exchange
How can we prove the formula [math]\sum_{r=1}^{n}r^2=\frac{n}{6}(2n+1)(n+1)[/math] without using induction? - Quora





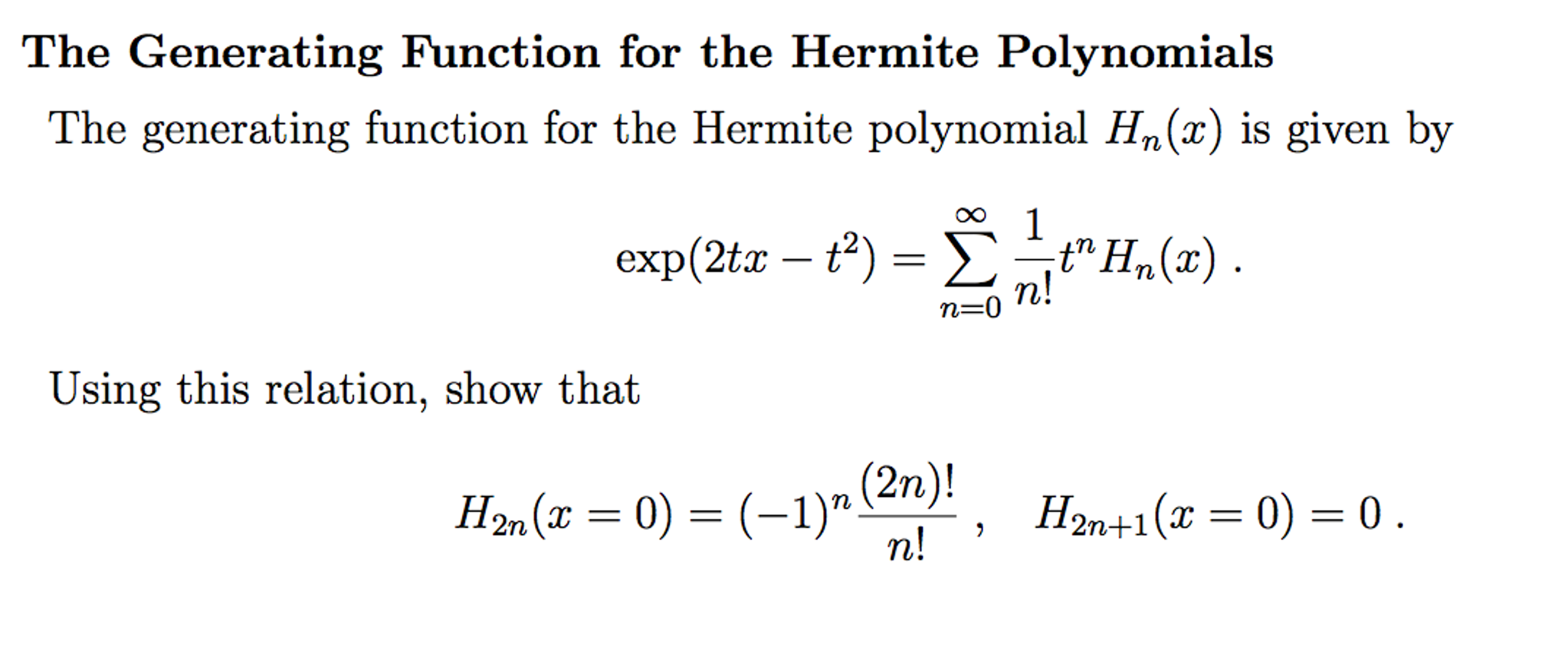


![Solved [RBH 18.4] Problem 1: Carry through the following | Chegg.com Solved [RBH 18.4] Problem 1: Carry through the following | Chegg.com](https://media.cheggcdn.com/media/12d/12d20fbd-2d77-4a22-be75-f2ae6ee781d2/phpFGlbZy.png)










